Young Pt with breast lump; next step after History & Examination……….. US.
Old pts >40 with breast lump; next step after History & Examination…… Mammography.
1st inv of solid mass: core biopsy.
Best inv of solid mass: excision.
1st inv of cystic mass: FNABC.
Asymptomatic mass in young female, hypoechoic on US: FIBROADENOMA.
TTT of fibroadenoma: surgery.
Young pt with breast Pain, swelling which fluctuate with menses: fibro-cystic disease of breast (fibro-adenosis).
TTT of fibro-adnosis: analgesic& tight fitting bra 1st, if no response: OCPs.
TTT of Severe fibro-adenosis not respond to OCPs: danazole.
MCC of bloody discharge of breast: intra-ductal papilloma.
TTT of Lactating female with mastitis: continues breast feeding.
1st: Breast feeding from affected side and then, from the other side.
If mastitis complicated by breast abscess: continues breast feeding from affected side 1st.
Gynecomastia in infant: passage of maternal hormones…… reassure.
Gynecomastia in puberty with pain& induration…………….. reassure.
Gyenecomastia in young athlete……………………………………. Steroid abuse.
Senile gynecomastia………………………………………………………… testosterone replacement.
Pt with viscid secretion (serous or creamy discharge) from breast: mammary duct ectasia.
Most common cause of bleeding per nipple…….duct papilloma
Mutation of BRCA1, BRCA2 gene increases risk of breast& ovarian cancer.
Old female with any change in her breast, skin overlying it, nipple, nipple discharge… most probable diagnosis is breast cancer (whatever other choices).
Screening of breast cancer: mammography (cancer appears as micro-calcification).
Mammography is done every 2 ys to all female from age 50
When to do mammo before 50 ys? if she asks or if FH of breast cancer in 1st degree <50 ys.
Why are Australian females are scared of mammo? pain.
Routine self breast examination is NO longer recommended.
Female with strong positive FH of breast, ovarian cancer… do gene assesment.
Female with one relative has brca mutation… do gene assesment.
Before doing BRCA1, BRCA2 test: do counseling about the test 1st.
After TTT of Women with breast cancer in one side, she develops breast cancer in the other side; the most probable cause is: 1ry cancer (not metastases from the other part).
Most imp prognostic factor of breast cancer: LN.
Main line of management of breast hematoma: excision.
N.B: for breast
Haw to deal with breast mass:
- First step …. Hestory & examination
- 2nd step ………. Imagin
- If young ……. U/S
- Old .. mammografy
- If solid mass: …… core biopsy
…..initial step
- Exisional biopsy … invest of choise
- F cystic lesion ……… aspiratin
- Fibroadenoma : young female with breast mass … invest. U/S
- Fibroadenosis : painfull swelling in breast increased befor period
TTT : analgesics , If failed : Danazol
- Intraductal papilloma : most common cause of bleeding discharge per nipple.
- Mastitis and Acute breast abscess :
TTT: antibiotics
Incision and drainage for B. abscess
Continue breast feeding from affected breast and start wit it 1st
If suction for milk she can feed the baby from it
- Gynecomastia : ask for steroids and anabolic hormons in young atheletic male.
- Mamary ductectasia : yellow serous or creemy white discharg.
- Breast cancer:
…General role: any old female with any breast abnormality … cancer breast untill prove other wise.
-Duct carcinoma ….. most common.
-Lobular carcinoma ….. bilateral.
-BRCA1 , BRCA2 : done if there is strong 1st degree +ve family history.
- Screeaning for breast cancer :
Mammography : all female 50-74 y every 2 years
Age 40-49 :
1-if she asked
2-if 1st degree +ve family history of breast cancer <50 y and do it annually.
- Pagets disease : old woman with unilateral nipple discharge.
- Breast hematoma : hard some times painfull mass with history of truma …. TTT : excision.
- Women with history of cancer breast at one side now come with cancer in other side ….. primary cancer not metastasis.
- Why female in aust. Scared from mammograohy…..pain.
How to deal with breast lump??????
First step………….history and examination
Imaging:
If young…………US
If old………mammography
if solid mass: 1st inv………….Core biopsy
Best inv……..excision
If cystic lesion………1st inv………aspirate
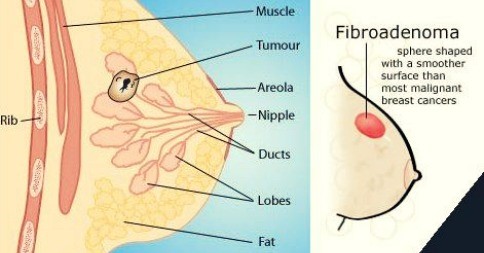
Fibroadenoma
Cp:
Young women
Firm, smooth and mobile
Usually asymptomatic, not painful
Inv………. Ultrasonography……hypoechoic mass
Treatment………surgery
Fibroadenosis(mammary dysplasia)
Hormone related disorder
Age 30-50
Pain, tenderness and swelling
Increased symptoms premenstrual
Fluctuation in the size of the mass….vvv imp
Nodular feeling and possible obvious lump
Inv………mammography and needle biopsy
If cyst………needle aspiration
Treatment…………. Analgesics
Tight bra
ocp
severe cases……..danazol……vvvvvvv imp
Intraductal papilloma
Most common cause of bloody discharge per nipple
Inv: mammography…exclude cancer
TTT…..duct excision
Mastitis
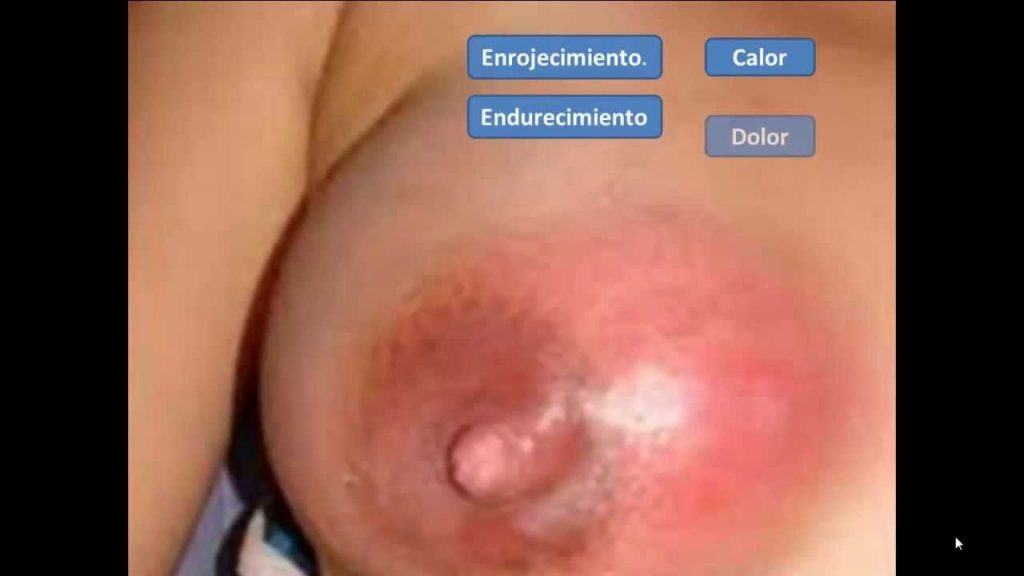
Causative organism…….staph
Pain and fever
Exam……engorgement and induration
TTT…..
SUPPORT breast to decrease pain
Hot bags and antibiotics
Continue breast feeding…..from affected breast 1st
Acute breast abscess
Severe and throbbing pain
Hectic fever
Marked systemic manifestation
Fluctuation
TTT…… incision under anesthesia
Leave a drain
Antibiotics
Continue breast feeding from affected side 1st
GYNECOMASTIA
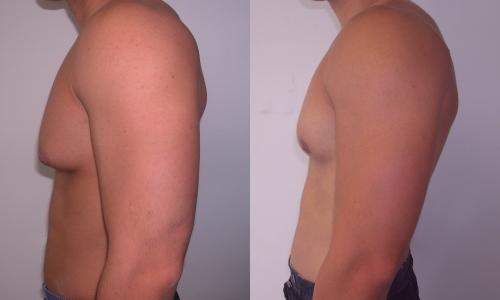
Infantile:
Cause……maternal estrogen
Prognosis….resolve within 6 months
Pubertal mastitis
Very common affect more than 50% of teenagers
Cp….pain swelling and induration
TTT…..REASSURE
Senile :
Cause reduction in testicular function
TTT…… Testosterone replacement
N:B:
If young male ATHELETE………steroid abuse
Drugs :
Anabolic ( Steroid , Amiodarone )
Cimetidine
Digoxin
Estrogen
Spironolactone
TCA
Mammary ducat ectasia
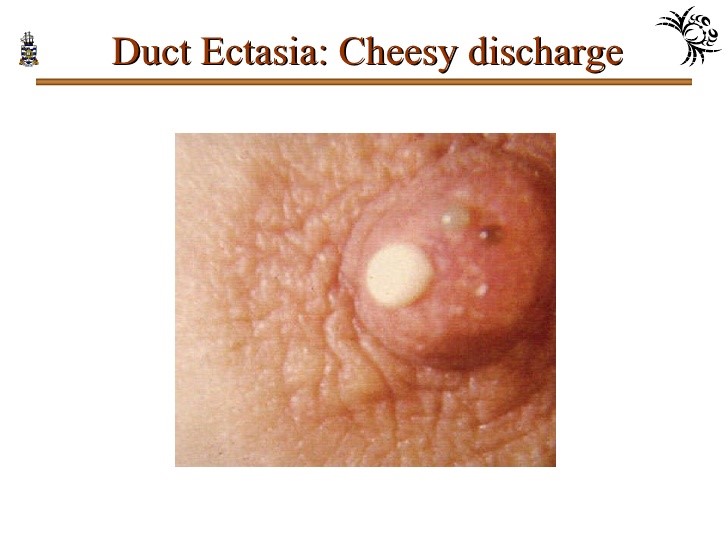
Cause…dilatation of major ducts
Cp:
Discharge….yellow, serous or creamy white
Retraction of the nipple
TTT……excision
Carcinoma of the breast:
Risk factors
Old age
Early menarche
Late menopause
Late first pregnancy
Nullipara
Atypical epithelial hyperplasia
Family history
+ BRCA1 AND BRCA2
Most common site……upper outer quadrant
Types:
Ductal carcinoma….most common
Lobular carcinoma…(bilateral)
Inflammatory carcinoma….rare, very invasive resemble mastitis
Pagets disease:
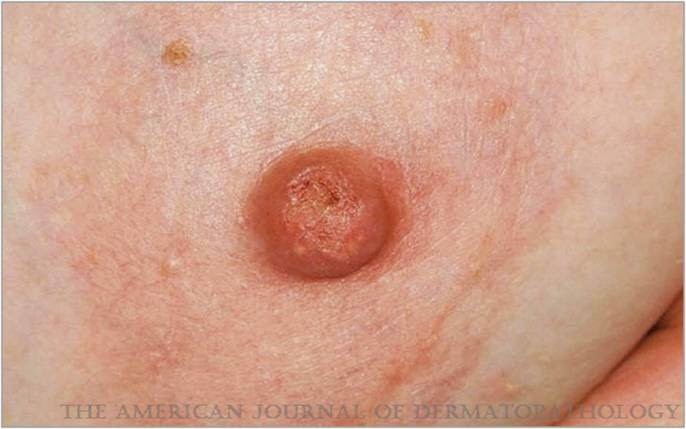
Type….intraductal carcinoma
Shape….nipple erosion
Mass….no palpable mass
Clinical picture of breast cancer:
Usually painless breast mass
Breast…..enlargement, asymmetry
Skin…..dimpling, ulceration or nodules
Nipples….retraction or change of direction
Lymph nodes/……enlargement
Paeu de orange…..advanced stage, non pitting edema due to obstruction of skin lymphatics
Investigation:
Imaging of choice………Mammography
Cancer appears with microcalcification and speculated appearance
Biopsy:
Core biopsy……………… initial
Excisional…………………..Best
When to do BRCA1 OR BRCA2 test?
First step…….counselling about the test
Positive family history (less than 50 years) breast or ovarian
Breast and ovarian cancer in the same female
Family history of male breast cancer
Is breast self exam routinely advised??….noooo
Has no effect on mortality rate
Best diagnostic screening tool decreasing mortality in whole preventive medicine……mammography
Screening for breast cancer:VVVVVVVVV IMP
Tool……..MAMMOGRAPHY
Routine:
All females from 50-74 every 2 years
Age 40-49…….1-only if she asked
2-1st degree less than 50 ys with breast cancer→( annually)
Age more than 74.…..only if she asked
When to screen at young age??
- One first degree relative with breast cancer in age younger than 50 years
- 2- 2- two first degree relatives with breast cancer at any age
- 3- 3- two second degree relatives less than 50
- 4- 2 first or second degree with the following:
Breast cancer less than 40 years
Bilateral breast cancer
Breast and ovarian cancer in the same female
Male breast cancer
Breast hematoma:
History of trauma or operations
Cp…….hard and some times painful mass
Breast biopsy…..fat globules
TTT..
EXCISION…..vvvvvvvvvvvvvvv imp
N:B:
Women with cancer breast in one side ….now has breast cancer on the other side ……what is the most probability………primary cancer not metastasis
Most imp prognostic factor of breast cancer……..LN
Why females in Australia are scared from mammograpgy…..pain…vvvvvvvvvvvvvv imp
